Tutorial 7
This week we will learn how we create a dynamic Web-App
Flask templates
Previously we learnt how to make a function return a string thats is printed in the browser like the following
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return ("hello world")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
if you run the previous code and typed http://127.0.0.1:5000 in your browser you should see “hello world””
instead of returning a string we want to ask the function to redirect us to html file using render_template function as following.
Now create a new folder called Flask in which you should create an empty server.py file and empty folder called templates. then create empty file called index.html inside the templates folder.
- Flask
- Server.py
- templates
- index.html
- open index.html file and insert the following:
- index.html
<p>This is the first html file</p>
- open server.py and insert the following:
from flask import Flask, render_template
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_name():
return render_template('index.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
so what happens now?! When you open your browser and write http://127.0.0.1:5000 flask will direct the browser to the index.html file
HTML
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language. HTML describes the structure of a Web page. HTML consists of a series of elements. HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content. HTML elements are represented by tags.
HTML file main structure:
<!DOCTYPE html>declares document file is a html file<html> </html>any thing in between these tag opening and ending are in the same web page<head> </head>element contains meta information about the document<title> </title>element specifies a title for the document<body> </body>element contains the visible page content
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
"" here is go our html code""
</body>
</html>
Warming up with few tags
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is heading 1 tag</h1>
<h2>This is heading 2 tag</h2>
<h3>This is heading 3 tag</h3>
<h4>This is heading 4 tag</h4>
<h5>This is heading 5 tag</h5>
<h6>This is heading 6 tag</h6>
<p>This is a paragraph</p>
<a href="actual link www.something.com">link text</a>
<table >
<tr>
<th>Header1</th>
<th>Header2</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Header 1 data</td>
<td>Header 2 data</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Header 1 data</td>
<td>Header 2 data</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
Now lets go back to our flask file and update index.html file. Now we will make two links at flask home page each of them directs to different function in flask.
- open index.html and write these line
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://127.0.0.1:5000/adddoctor">Add doctor</a>
<a href="http://127.0.0.1:5000/viewdoctor">View Doctor</a>
</body>
</html>
this a html file contain two links each open calls a different url in flask application. now run your server you should see both links but if clicked any one of them. it will gives you an error because we didn`t define it yet
- modify the server.py application:
from flask import Flask, render_template
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_name():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/adddoctor')
def adddoctor():
return render_template('adddoctor.html')
@app.route('/viewdoctor')
def viewdoctor():
return render_template('viewdoctor.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
now the server file have two new function each one is called and direct to a new hml file. lets create these new html files adddoctor.html , viewdoctor.html.
- Flask
- server.py
- templates
- index.html
- adddoctor.html
- viewdoctor.html
- open adddoctor.html and write
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is add doctor tap</h1>
<a href="http://127.0.0.1:5000">Back</a>
</body>
</html>
- open viewdoctor.html and write
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is view doctor tap</h1>
<a href="http://127.0.0.1:5000">Back</a>
</body>
</html>
Now you can run your server and click links to show how they make flow through your application.
HTML forms
The HTML <form> element defines a form that is used to collect user input:
<input>is used to collect user input- type attribute is used to define input type
- name attribute is used to define the input name to be used inside functions
- action attribute to define a destination for the data
- method defines the method of http protocol: which is the foundation of data communication in world wide web. Different methods of data retrieval from specified URL are defined in this protocol.
- GET: Sends data in un-encrypted form to the server. Most common method
- POST: Used to send HTML form data to server. Data received by POST method is not cached by server. Hint: Links directly used GET method when calls a link
<form action="where the data is going(a link or function)" method="GET or POST">
First name:<br>
<input type="text" name="firstname" value="Mickey"><br>
Last name:<br>
<input type="text" name="lastname" value="Mouse"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Now lets modify our adddoctor function to actually take user input and commit it to database
First: Lets create doctor tables in our database
import mysql.connector
mydb = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
passwd="mysql",
database="MyPythonDatabase"
)
mycursor = mydb.cursor()
mycursor.execute("CREATE TABLE Doctors (name VARCHAR(255),department VARCHAR(255), id INT, PRIMARY KEY(id))")
Next: We modify our add doctor.html file to the following
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is add doctor tap</h1>
<form action="http://localhost:5000/adddoctor" method="POST">
name:<br>
<input type="text" name="name" value="example">
<br>
department:<br>
<input type="text" name="department" value="radiology">
id<br>
<input type="number" name="id" value="10">
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<a href="http://127.0.0.1:5000">Back</a>
</body>
</html>
Now Lets modify our server.py to receive form data and print it in the terminal temporary and direct us to index.html after printing
from flask import Flask, render_template,request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_name():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/adddoctor',methods = ['POST', 'GET'])
def adddoctor():
if request.method == 'POST': ##check if there is post data
name = request.form['name']
department = request.form['department']
id = request.form['id']
print(name,department,id)
return render_template('index.html')
else:
return render_template('adddoctor.html')
@app.route('/viewdoctor')
def viewdoctor():
return render_template('viewdoctor.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
Now yoy can run your server and tap the add doctor link then write some date. When you click submit button it will redirect you to home page and you should see the data printed in the terminal.
Lets push these data into the data base table Doctors: modify your server.py for the following
import mysql.connector
from flask import Flask, redirect, url_for, request,render_template
mydb = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
passwd="mysql",
database="MyPythonDatabase"
)
mycursor = mydb.cursor()
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_name():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/adddoctor',methods = ['POST', 'GET'])
def adddoctor():
if request.method == 'POST': ##check if there is post data
name = request.form['name']
department = request.form['department']
id = request.form['id']
print(name,department,id)
sql = "INSERT INTO Doctors (name,department, id) VALUES (%s, %s, %s)"
val = (name,department,id)
mycursor.execute(sql, val)
mydb.commit()
return render_template('index.html')
else:
return render_template('adddoctor.html')
@app.route('/viewdoctor')
def viewdoctor():
return render_template('viewdoctor.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
Template rendering
render_template function is used not only to redirect a request to a html file but also it can send variable with it
Lets modify viewdoctor function to redirect and send a message
import mysql.connector
from flask import Flask, redirect, url_for, request,render_template
mydb = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
passwd="mysql",
database="MyPythonDatabase"
)
mycursor = mydb.cursor()
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_name():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/adddoctor',methods = ['POST', 'GET'])
def adddoctor():
if request.method == 'POST': ##check if there is post data
name = request.form['name']
department = request.form['department']
id = request.form['id']
print(name,department,id)
sql = "INSERT INTO Doctors (name,department, id) VALUES (%s, %s, %s)"
val = (name,department,id)
mycursor.execute(sql, val)
mydb.commit()
return render_template('index.html')
else:
return render_template('adddoctor.html')
@app.route('/viewdoctor')
def viewdoctor():
mes = "this is my first message"
return render_template('viewdoctor.html',message=mes)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
Then we modify viewdoctor.html to the following:
- the curly braces is used to print variables sent from flask
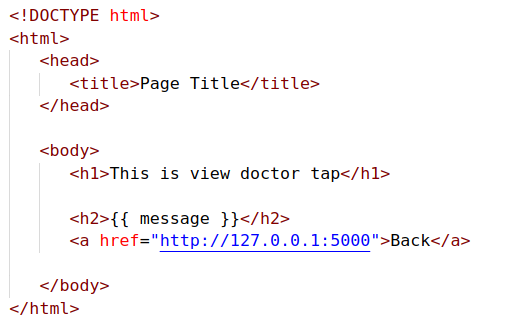
We can also send some data from the database not only a static message. Modify server.py for the following to retrieve doctors and send it to viewdoctor taps
import mysql.connector
from flask import Flask, redirect, url_for, request,render_template
mydb = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
passwd="mysql",
database="MyPythonDatabase"
)
mycursor = mydb.cursor()
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_name():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/adddoctor',methods = ['POST', 'GET'])
def adddoctor():
if request.method == 'POST': ##check if there is post data
name = request.form['name']
department = request.form['department']
id = request.form['id']
print(name,department,id)
sql = "INSERT INTO Doctors (name,department, id) VALUES (%s, %s, %s)"
val = (name,department,id)
mycursor.execute(sql, val)
mydb.commit()
return render_template('index.html')
else:
return render_template('adddoctor.html')
@app.route('/viewdoctor',methods = ['POST', 'GET'])
def viewdoctor():
if request.method == 'POST':
return render_template('index.html')
else:
mycursor.execute("SELECT * FROM Doctors")
row_headers=[x[0] for x in mycursor.description] #this will extract row headers
myresult = mycursor.fetchall()
data={
'message':"data retrieved",
'rec':myresult,
'header':row_headers
}
return render_template('viewdoctor.html',data=data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
Lastly We modify viewdoctor.html file as the following
