Week 12: Introduction to Image Processing
- Fundamental Block Diagram of Image Processing
- Image Acquisition
- Digital Image
- Resizing images
- Image Enhancement
- Image Segmentation
- Recognition and Interpretation
Fundamental Block Diagram of Image Processing

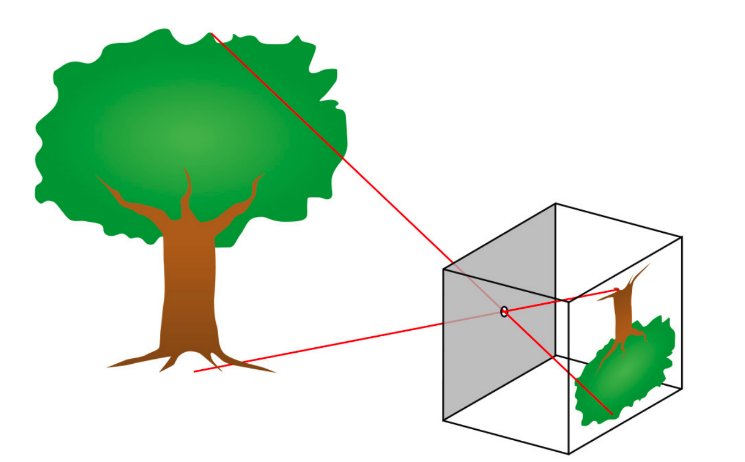
Image Acquisition
Digital Camera
- Matrix of CCD elements (photodiodes)
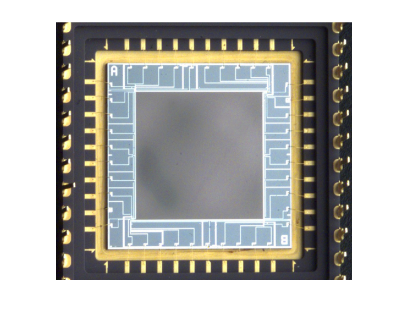
- Each pixel has 4 sensors (1 Red, 1 Blue, 2 Green)
![]()
- Image projection
Digital Image
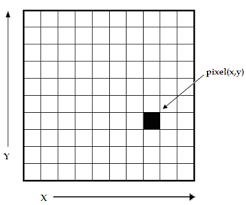
- Digital image is a matrix of pixels Color of each pixel is determined by its RGB values

- For grayscale images only one channel determine the gray level

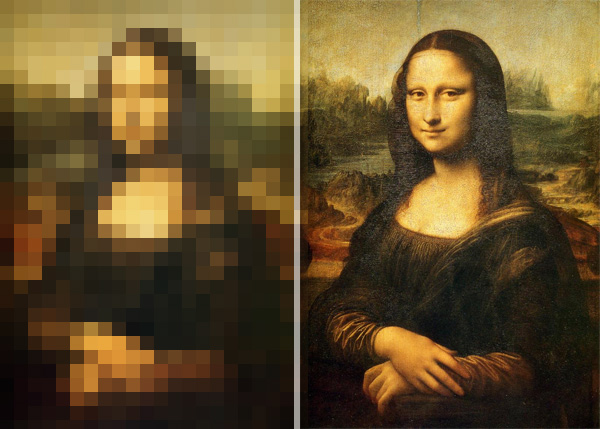
Resizing images
The Original Image
from scipy.misc import imresize
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
im = plt.imread('black-dog.png')
Resize the image
resizeFactors = [1, 0.2, 0.1, 0.05]
for factor in resizeFactors:
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(imresize(im, (int(im.shape[0]*factor), int(im.shape[1]*factor))))
plt.title('Resized image with factor ' + str(factor))
plt.show()
The output
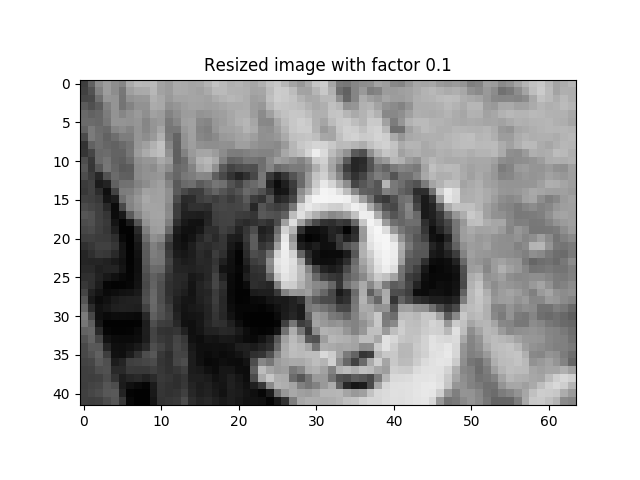



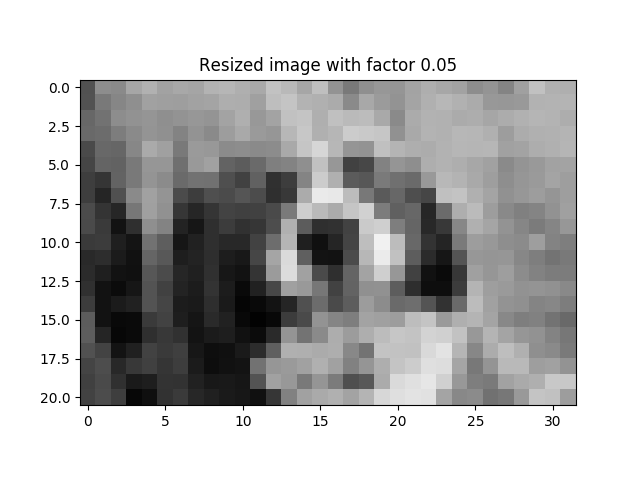
Image Enhancement
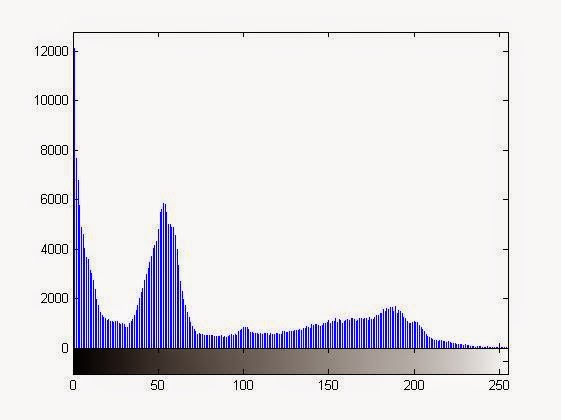
- Enhancing image contrast using histogram equalization.
- Histogram is the number of pixel for each intensity value.
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('PgaNb.png',0)
equ = cv2.equalizeHist(img)
res = np.hstack((img,equ)) #stacking images side-by-side
cv2.imwrite('res.png',res)
Output

Image Segmentation
- Convert the image to segments or isolated objects
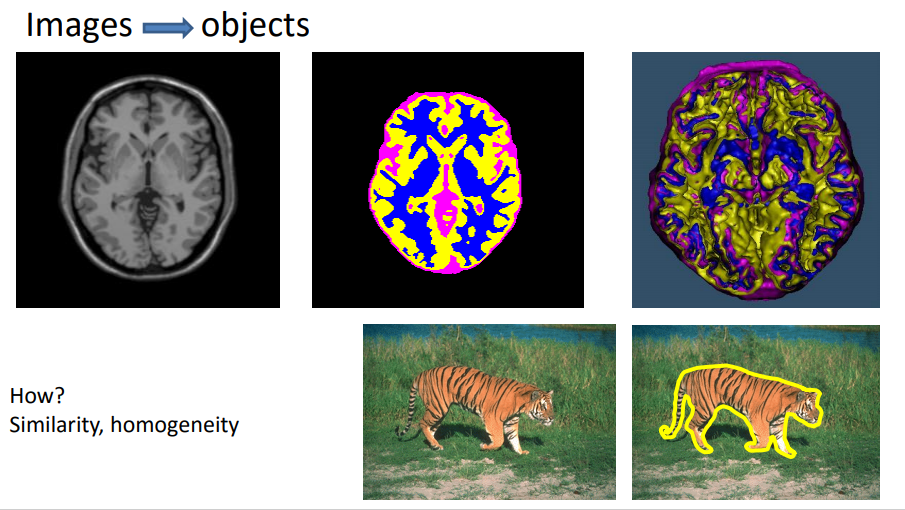
- Thresholding is the basic technique that segments the image into two classes object and background

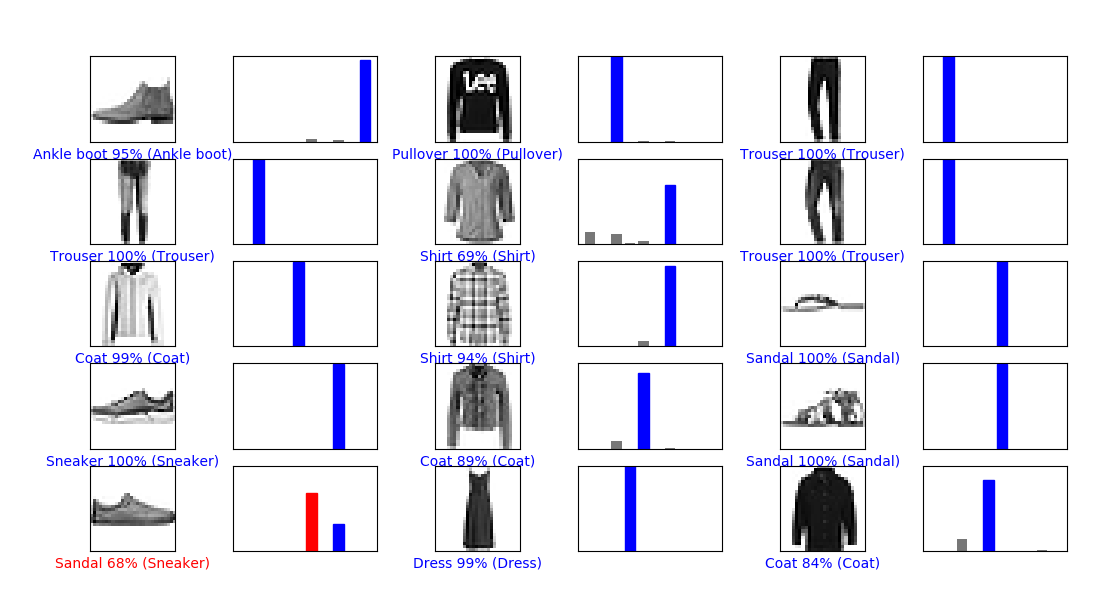
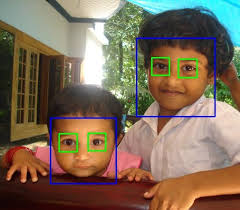
Recognition and Interpretation
- Face and eye detection
- Person detection

- Object detection (car)

- Object recognition

- Machine learning and classification