Ray Casting, Lightening & Animation
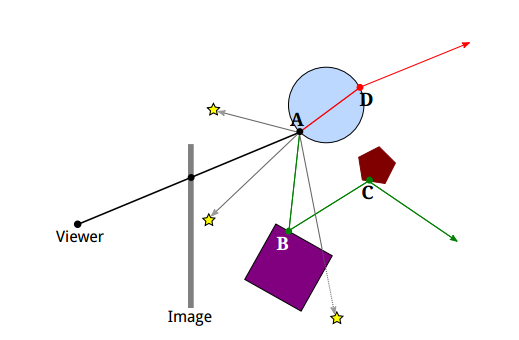
Ray Casting
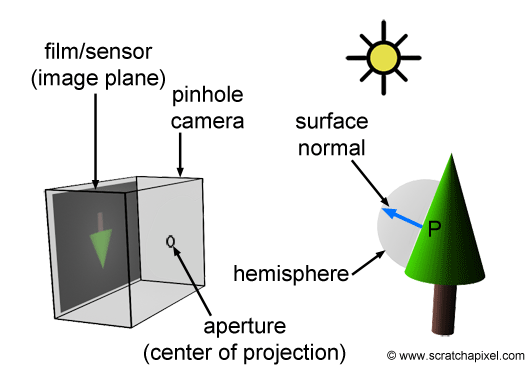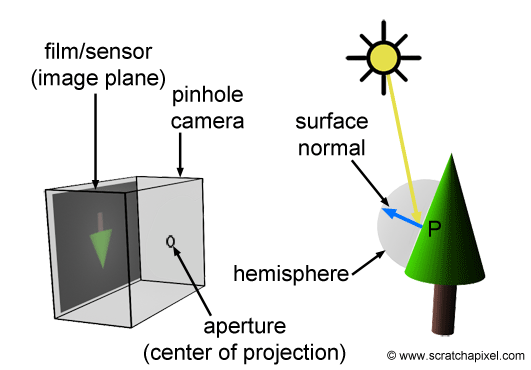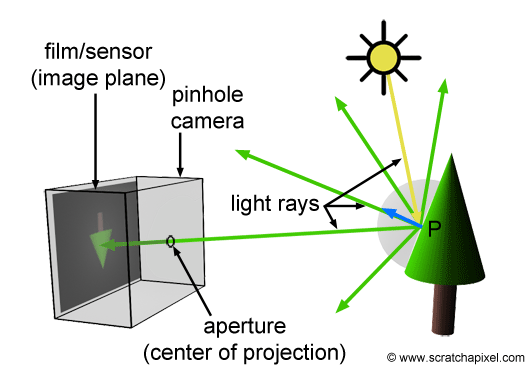
Vision Process
In human vision process is as follow
- Lights drop on objects
- Then it is reflected (scattered) in all directions
- Reflected light rays are received by the eye and image is formed.
The same is for the pinhole camera model
Ideally
- There is an infinite number of rays
- Multiple reflections happen for the same ray on different objects
So how we simulate this in computer graphics ? Keep in mind that the objective is to get a 2D image of the scene.
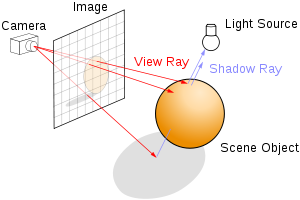
Ray Casting
Basic Idea The process is reversed where rays are sent from the camera position instead of receive it at the camera position.
Pseudo code for ray casting
for each pixel:
Send a ray through the scene
Find the interection with objects
Calculate the color at this intersection
Assign this color to that pixel where ray was sent from
Ray Tracing
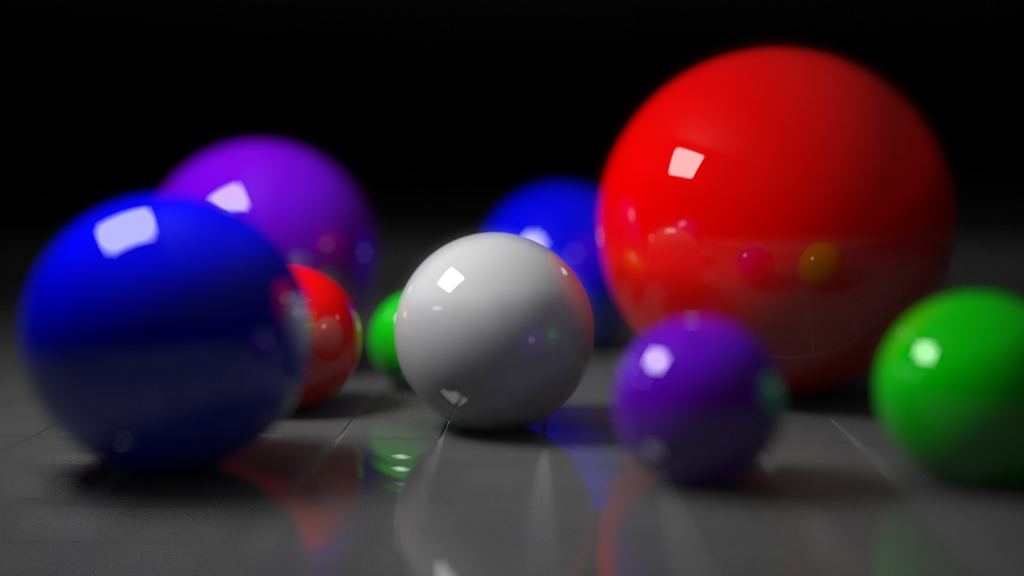
- It is the same idea with more complex calculations
-
Rays must be checked with all objects in the scene by tracking its reflections recursively.
-
It is computationally extensive and time-consuming process but has realistic results
- It is used for creating visual effects and not applicable in interactive applications (Games)
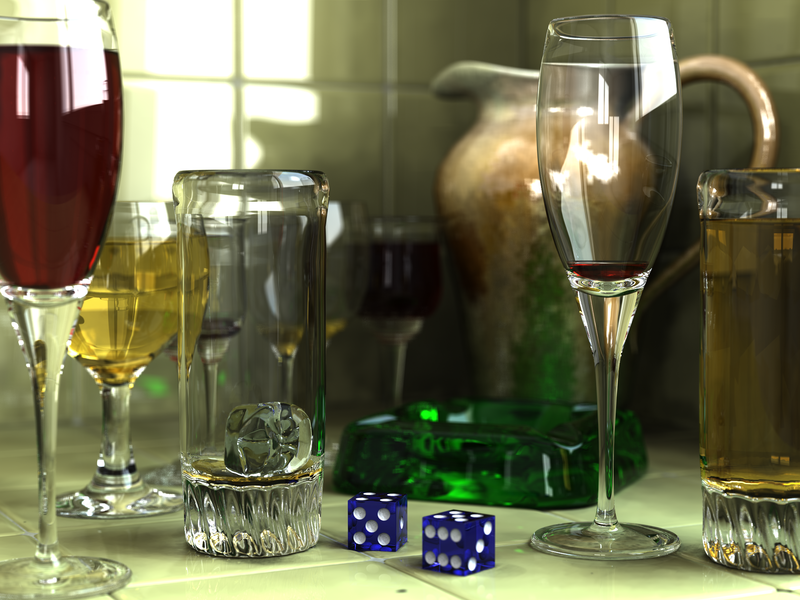
Sample of generated images with ray tracing (source)

Lighting
Classical lighting models
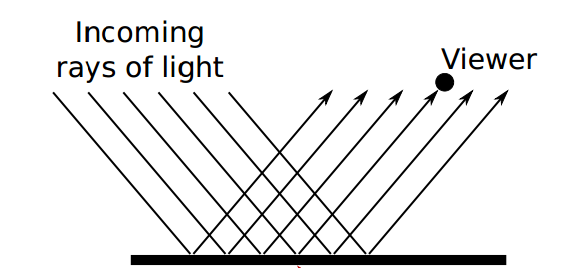
- Ambient lighting : It is an approximation of uniform light without a light source. It illuminate all objects equally.
- Diffuse lighting
The light is reflected in all direction due to the roughness of the surface.

- Specular lighting:
Reflection of the light in one direction (Smooth surface).
Enabling lightening in OpenGL
You need to define color properties and enable it.
// Here we have a white light source
float light_ambient[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
float light_diffuse[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
float light_specular[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
// This is the light position
float light_position[] = {0.0, 0.0, 4.0, 1.0};
// Setting light source properties and enabling it
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT1, GL_POSITION, light_position);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT1, GL_AMBIENT, light_ambient);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT1, GL_DIFFUSE, light_diffuse);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT1, GL_SPECULAR, light_specular);
glEnable(GL_LIGHT1);
glEnable(GL_LIGHTING);
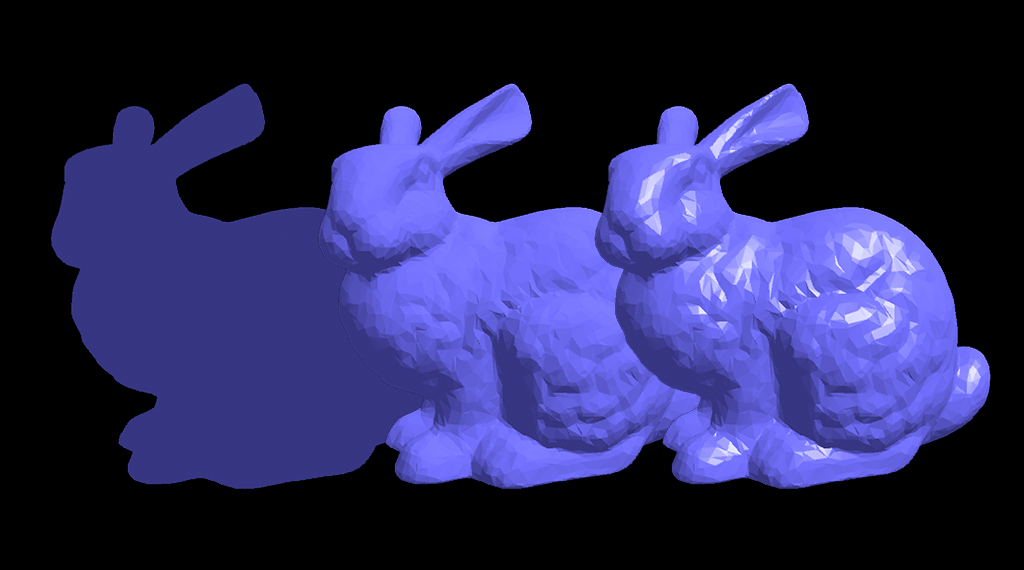
This is an example of a solid sphere
No light sources
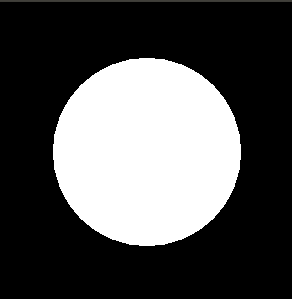
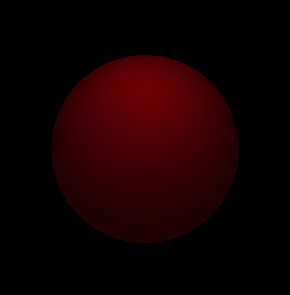
Only ambient is set

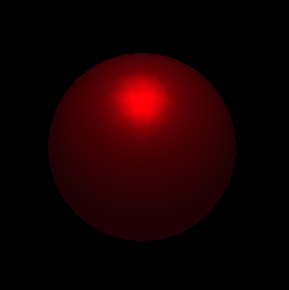
Ambient, diffuse
Ambient, diffuse, and specular
Animation Key concept
The key concept of animation is to compose a set of frame with different poses of the model and blend these frames one after another to get the object animated.
Think of it like video capturing. You capture multiple frames through time and view these frames in a specific rate (Frame rate).
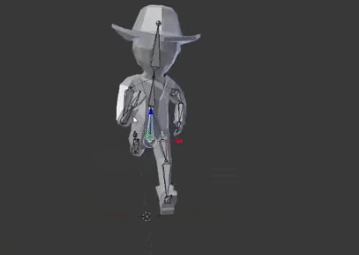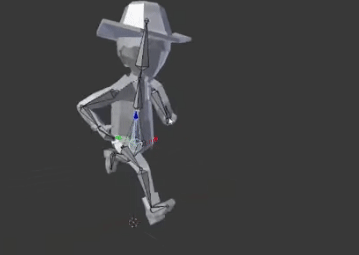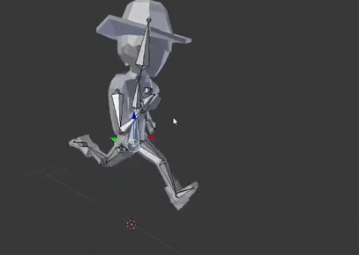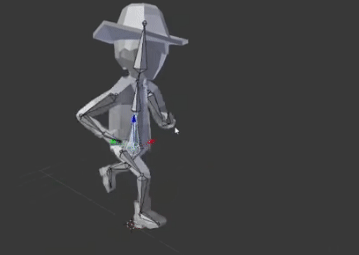
Frame by frame animation
For example this is first pose

And this is the second pose

And this is the third pose

and so on
When we run these poses with time it will seem that the object is moving.
Section Demo
All demos will be available in this repository