Week 7: Heap & Priority Queue (ADT)
- Heaps
- Heap Applications
- Glossary
- Operations
- Min-heap Implementation Using Arrays
- Implementation: Class Members
- Implementation: Storage Array
- Implementation: From Parent Index to Child Index + Vice versa
- Implementation: Heap size
- Implementation: Insert & SiftUp
- Implementation: Extract & SiftDown
- Implementation: Heapifying Arbitrary Array
- Complexity Analysis: Heapifying Arbitrary Array
- Final Implementation of Heap
- Heap Applications: Heapsort
- Download the source files
Heaps
- Heap is a very useful data structure with many applications (e.g Heapsort and Priority Queues (ADT)). Heap elements are typically allocated as a dynamic array. However, the elements are conceptually forming a complete tree.
| Max-Heap Logical Representation |
|---|
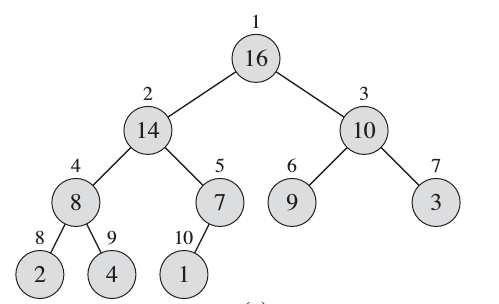 |
| Max-Heap Storage |
|---|
 |
| Max-Heap |
|---|
| Creative Commons - Maxinator |
Heap Applications
- Sorting Algorithms (Heapsort)
- The Shortest Path Problem (Dijkstra’s Algorithm)
- Data Compression Algorithms (Huffman Tree)
- Unsupervised Machine Learning (Agglomerative Clustering)
Glossary
- Complete Tree: A balanced tree in which the distance from the root to any leaf is either $\lfloor \log(n) \rfloor$ or $\lfloor \log(n)-1 \rfloor$. source.
Operations
Insert
Inserting an element at the end of the heap typically violates the heap property (i.e each parent is greater than its children for max-heaps), so after each insertion we need to recover back the heap property.
The algorithm of insertion (source: wikipedia):
- Insert the new element to the bottom level of the heap.
- Compare the added element with its parent; if they are in the correct order, stop.
- If not, swap the element with its parent and repeat step (2) recursively.
Example: Insert 15
| Steps | Layout |
|---|---|
| We first place the new element 15 in the position marked by the X as a leaf. | 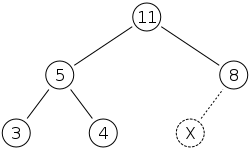 |
| However, the heap property is violated since 15 > 8, so we need to swap the 15 and the 8 | |
| The heap property is still violated since 15 > 11, so we need to swap again | |
| Source: wikipedia |
Extract
In a similar way to insertion, when we pop the maximum of max-heap (its root), we violate the heap property by replacing the last children in the heap to be the new root. In order to recover the heap property, we use the following procedures (source: wikipedia):
- Replace the root of the heap with the last element on the last level.
- Compare the new root with its children; if they are in the correct order, stop.
- If not, swap the element with one of its children and repeat step (2). (Swap with its smaller child in a min-heap and its larger child in a max-heap.)
| Steps | Layout |
|---|---|
| Extract element 11. | |
| 11 is replaced by the the left-most leaf 4. | |
| Heap property is violated (8 is greater than 4). Swapping the two elements 4 and 8 is enough to recover the heap. | |
| Source: wikipedia |
Min-heap Implementation Using Arrays
Implementation: Class Members
template< typename T >
class Heap
{
public:
size_t size() const
{
// Return heap size
}
void insert(T value)
{
// 1. Insert as leaf
// 2. Recover heap properties
}
T extract()
{
// 1. Extract the root
// 2. Recover heap properties
}
private:
// Private methods
private:
// Private data members
};
Implementation: Storage Array
template< typename T >
class Heap
{
public:
// Return heap size
size_t size() const {}
// 1. Insert as leaf
// 2. Recover heap properties
void insert(T value){}
// 1. Extract the root
// 2. Recover heap properties
T extract(){}
private:
// Private methods
private:
// Private data members
std::vector< T > data;
};
Implementation: From Parent Index to Child Index + Vice versa
template< typename T >
class Heap
{
public:
// Return heap size
size_t size() const {}
// 1. Insert as leaf
// 2. Recover heap properties
void insert(T value){}
// 1. Extract the root
// 2. Recover heap properties
T extract(){}
private:
// Private methods
static size_t leftChildIdx(size_t parent)
{
return parent * 2 + 1;
}
static size_t rightChildIdx(size_t parent)
{
return parent * 2 + 2;
}
static size_t parentIdx(size_t child)
{
if (child % 2 == 1)
return (child - 1) / 2;
else
return (child - 2) / 2;
}
private:
// Private data members
std::vector< T > data;
};
Implementation: Heap size
template< typename T >
class Heap
{
public:
// Return heap size
size_t size() const { return data.size();}
// 1. Insert as leaf
// 2. Recover heap properties
void insert(T value){}
// 1. Extract the root
// 2. Recover heap properties
T extract(){}
private:
// Private methods
static size_t leftChildIdx(size_t parent){... }
static size_t rightChildIdx(size_t parent){... }
static size_t parentIdx(size_t child){... }
private:
// Private data members
std::vector< T > data;
};
Implementation: Insert & SiftUp
- The
insertoperation adds a new node as the left-most leaf - To recover the heap properties the
siftUpis applied on the new node: if node is greater than its parent, then heap is satisfied and terminate, otherwise, swap the node with parent and repeat recursively.
- Worst case time: to go up along all levels $h= \lfloor \log(n) \rfloor$.
- $O(T(n)) = O(h) = O(\log(n))$
template< typename T >
class Heap
{
public:
// Return heap size
size_t size() const { return data.size();}
void insert(T value)
{
data.push_back(value);
size_t childIdx = size() - 1;
siftUp( childIdx ); // Recover heap
}
// 1. Extract the root
// 2. Recover heap properties
T extract(){}
private:
// Private methods
void siftUp( size_t child )
{
auto parent = parentIdx(child);
if( child > 0 && data[child] < data[parent])
{
std::swap(data[child], data[parent]);
siftUp( parent );
}
}
static size_t leftChildIdx(size_t parent){... }
static size_t rightChildIdx(size_t parent){... }
static size_t parentIdx(size_t child){... }
private:
// Private data members
std::vector< T > data;
};
Implementation: Extract & SiftDown
- The
extractoperation removes the root and replace it by the left-most leaf. - To recover the heap properties the
siftDownis applied on the new root: if root is less than its children, then heap is satisfied and terminate, otherwise, swap the root with the minimum children and repeat recursively.
- Worst case time: to go down along all levels $h= \lfloor \log(n) \rfloor$.
- $O(T(n)) = O(h) = O(\log(n))$
template< typename T >
class Heap
{
public:
// Return heap size
size_t size() const { return data.size();}
void insert(T value){... }
// 1. Extract the root
// 2. Recover heap properties
T extract()
{
if( data.empty())
{
std::cout << "Empty Heap!\n";
exit( 1 ); // Crash
}
size_t child = size() - 1;
std::swap(data[child], data[0]);
T value = data.back();
data.pop_back();
siftDown(0);
return value;
}
private:
// Private methods
void siftUp( size_t child ){... }
void siftDown( size_t parent)
{
size_t left = leftChildIdx(parent);
size_t right = rightChildIdx(parent);
size_t length = size();
size_t minimum = parent;
if (left < length && data[left] < data[minimum])
minimum = left;
if (right < length && data[right] < data[minimum])
minimum = right;
if (minimum != parent)
{
std::swap(data[minimum], data[parent]);
siftDown( minimum );
}
}
static size_t leftChildIdx(size_t parent){... }
static size_t rightChildIdx(size_t parent){... }
static size_t parentIdx(size_t child){... }
private:
// Private data members
std::vector< T > data;
};
Implementation: Heapifying Arbitrary Array
template< typename T >
class Heap
{
public:
size_t size() const{... }
void insert(T value){... }
T extract(){... }
static Heap make( std::vector< T > data )
{
Heap h;
h.data.swap( data ); // O(1)
if( h.size() <= 1 ) return h;
auto lastChild = h.size() - 1;
for( int subHp = parentIdx( lastChild ); subHp >= 0 ; --subHp )
h.siftDown( subHp );
return h;
}
private:
// Private methods
void siftUp( size_t child ){... }
void siftDown( size_t parent){... }
static size_t leftChildIdx(size_t parent){... }
static size_t rightChildIdx(size_t parent){... }
static size_t parentIdx(size_t child){... }
private:
// Private data members
std::vector< T > data;
};
Complexity Analysis: Heapifying Arbitrary Array
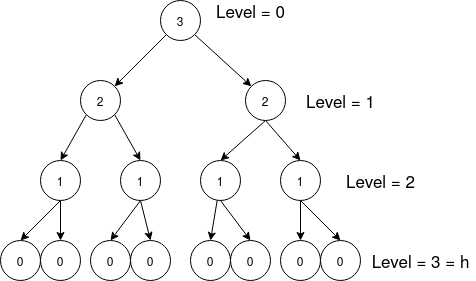
| Level | #Sub_Heaps | Heapify Cost |
|---|---|---|
| $h$ | $2^h$ | 0 |
| $h-1$ | $2^{h-1}$ | 1 |
| … | … | … |
| 1 | 2 | $h-1$ |
| 0 | 1 | $h$ |
Time Growth Function \(T(n)\) for heapifying all nodes:
\[T(n) = 2^h \times 0 + 2^{h-1} \times 1 + \ldots + 2^0 \times h = \sum_{j=0}^h j 2^{h-j} \label{eq:tn}\tag{E1}\]Useful Equations
- The relation between
- \(h\): the height of a full binary tree and
- \(n\): the number of nodes:
- The power series: \(\begin{equation} \sum_{j=0}^{\infty} x^j = \frac{1}{1-x}; |x|<1 \label{eq:PS1}\tag{PS1} \end{equation}\)
- Differentiating Equation \eqref{eq:PS1} with respect to \(x\) yields: \(\begin{align*} \sum_{j=0}^{\infty} j x^{j-1} &= \frac{1}{(1-x)^2} \\ \quad &\textrm{multiplying by x:} \quad \\ \sum_{j=0}^{\infty} j x^{j} &= \frac{x}{(1-x)^2} \label{eq:PS2}\tag{PS2} \end{align*}\)
Evaluating \(T(n)\) & \(O(n)\)
From \eqref{eq:tn} we estimated $T(n)$ as: \(\begin{align*} T(n) &= \sum_{j=0}^h j 2^{h-j} \\ &= \sum_{j=0}^h j \frac{2^h}{2^j} \\ &= 2^h \sum_{j=0}^h \frac{j}{2^j} \\ \textrm{by substituting $x=\frac{1}{2}$ in \eqref{eq:PS2}:} \\ \sum_{j=0}^\infty \frac{j}{2^j} &= \sum_{j=0}^\infty j(\frac{1}{2})^j = \frac{\frac{1}{2}}{(1 - \frac{1}{2})^2} = 2 \\ \textrm{therefore: }& \\ 2^h \sum_{j=0}^h \frac{j}{2^j} &< 2^h \sum_{j=0}^\infty \frac{j}{2^j} = 2^h (2) \\ \textrm{therefore: } & \\ T(n) &< 2^{h+1} \\ \textrm{From \eqref{eq:nh}: } & \\ T(n) &< n + 1 \\ \textrm{therefore, the big-O notation of $T(n)$:}& \\ O(T(n)) &= O(n) \end{align*}\)
Final Implementation of Heap
Heap Applications: Heapsort
std::vector< int > heapSort( std::vector< int > a )
{
auto h = Heap<int>::make( a ); // Heapify: O(n)
a.clear();
while( h.size() > 0 ) // O( n * log(n) )
a.push_back( h.extract()); // O(log(n))
return a;
}
Time Complexity: \(O(T(n)) = O(n) + O(n\log(n)) = O(n\log(n))\)
Advanced: avoiding $O(n)$ deep copy
Advanced: avoiding $O(n)$ deep copy
std::vector< int > heapSort( std::vector< int > a )
{
auto h = Heap<int>::make( std::move( a ));
while( h.size() > 0 )
a.push_back( h.extract());
return a;
}
The first line in this function avoids making a deep copy of std::vector<int>. Also, a becomes empty after that line (very briefly: some other std::vector<int> has stolen the pointer to the internal raw array of a, and then updated a internal pointer to nullptr)
To understand what is happening:
Visualization & Links
| Heapsort |
|---|
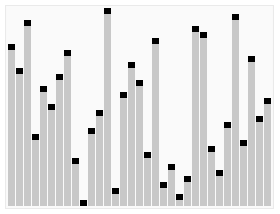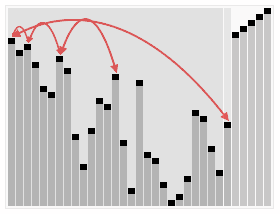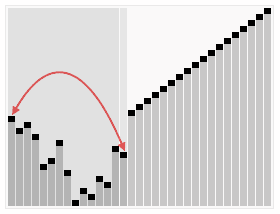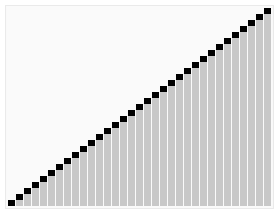 |
Download the source files
mkdir -p section07/Heap
cd section07/Heap
wget -i https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sbme-tutorials/sbme-tutorials.github.io/master/2020/data-structures/snippets/section07/Heap/download.txt
To build:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make