Week 8: Heaps, Priority Queues (ADT), and Shortest Path Problem
- Objectives
- Heaps
- Heapsort
- Reading Homework: Priority Queue (ADT)
Objectives
- Learn about heap structure
- Implementing heap using arrays
- Implementing priority queue (ADT) using heap
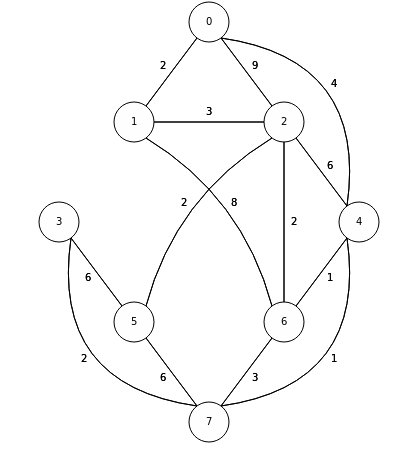
- The Shortest Path Problem (TSP)
Heaps
Heap is a very useful data structure which is potential in many applications (e.g Heapsort and Priority Queues (ADT)). Heap elements are typically allocated as a dynamic array. However, the elements are conceptually forming a complete tree.
| Heap as array |
|---|
| Creative Commons - Maxinator |
| Conceptual Representation |
|---|
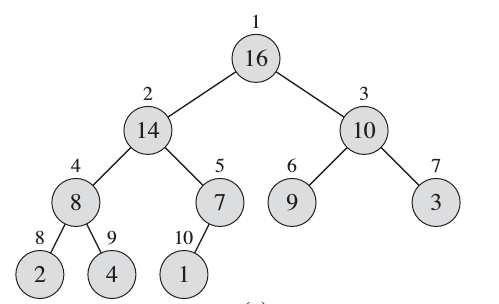 |
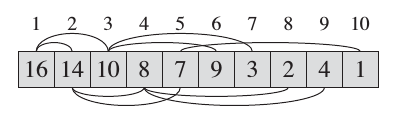 |
Glossary
- Complete Tree: A balanced tree in which the distance from the root to any leaf is either $log(n)$ or $log(n)-1$. source.
Operations
Insert
Inserting an element at the end of the heap typically violates the heap property (i.e each parent is greater than its children for max-heaps), so after each insertion we need to recover back the heap property.
The algorithm of insertion (source: wikipedia):
- Insert the new element to the bottom level of the heap.
- Compare the added element with its parent; if they are in the correct order, stop.
- If not, swap the element with its parent and repeat step (2) recursively.
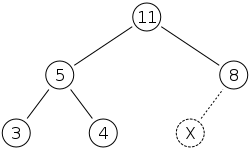
Example: Insert 15
| Steps | Layout |
|---|---|
 |
|
| We first place the 15 in the position marked by the X. However, the heap property is violated since 15 > 8, so we need to swap the 15 and the 8 | |
| However the heap property is still violated since 15 > 11, so we need to swap again | |
| Source: wikipedia |
Extract
In a similar way to insertion, when we pop the maximum of max-heap (its root), we violate the heap property by replacing the last children in the heap to be the new root. In order to recover the heap property, we use the following procedures (source: wikipedia):
- Replace the root of the heap with the last element on the last level.
- Compare the new root with its children; if they are in the correct order, stop.
- If not, swap the element with one of its children and repeat step (2). (Swap with its smaller child in a min-heap and its larger child in a max-heap.)
| Steps | Layout |
|---|---|
| We remove the 11 and replace it with the 4. | |
| Now the heap property is violated since 8 is greater than 4. In this case, swapping the two elements, 4 and 8, is enough to restore the heap property and we need not swap elements further | |
| Source: wikipedia |
Min-heap implementation using arrays
Implementation: Buffer
struct Heap
{
std::vector<int> buffer;
};
Implementation: Left Child Index
int getLeftIdx(int parent)
{
return parent * 2 + 1;
}
Implementation: Right Child Index
int getRightIdx(int parent)
{
return parent * 2 + 2;
}
Implementation: Parent Index
int getParentIdx(int child)
{
if (child % 2 == 1)
{
return (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
return (child - 2) / 2;
}
}
Implementation: Heap size
int size(Heap &h)
{
return h.buffer.size();
}
Implementation: Insert
void insert(Heap &h, int data)
{
h.buffer.push_back(data);
int childIdx = h.buffer.size() - 1;
bubbleUp( h , childIdx );
}
Implementation: Bubble-up / Sift-up / Cascade-up
void bubbleUp(Heap &h, int child )
{
int parent = getParentIdx(child);
if( child >= 0 && parent >= 0 && h.buffer[child] < h.buffer[parent])
{
std::swap(h.buffer[child], h.buffer[parent]);
bubbleUp( h , parent );
}
}
Implementation: Extract
int extract(Heap &h)
{
int child = h.buffer.size() - 1;
std::swap(h.buffer[child], h.buffer[0]);
int value = h.buffer.back();
h.buffer.pop_back();
bubbleDown( h , 0);
return value;
}
Implementation: Bubble-down / Sift-down / Cascade-down
void bubbleDown(Heap &h, int parent)
{
int left = getLeftIdx(parent);
int right = getRightIdx(parent);
int length = size(h);
int minimum = parent;
if (left < length && h.buffer[left] < h.buffer[minimum])
minimum = left;
if (right < length && h.buffer[right] < h.buffer[minimum])
minimum = right;
if (minimum != parent)
{
std::swap(h.buffer[minimum], h.buffer[parent]);
bubbleDown(h, minimum);
}
else return;
}
Clone the source code
git clone git@github.com:sbme-tutorials/sbe201-heap-pq.git
Heapsort
| Heapsort |
|---|
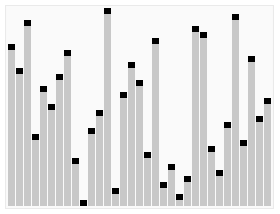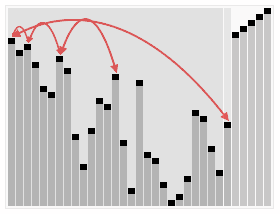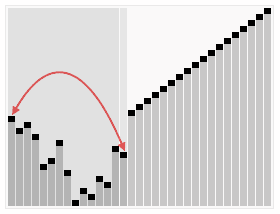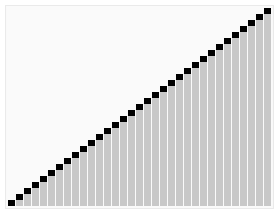 |
| Creative Commons - de:User:RolandH |
Reading Homework: Priority Queue (ADT)
- What is PQ as an ADT.
- How can be implemented using Heap.
- Applications.
Reading Homework: Shortest Path Problem
- What is shortest path problem.
- Dijkstra’s algorithm using PQ.
- Applications of Dijkstra.
Exercise: Dijkstra