Introduction to Computer Graphics
Introduction to Computer Graphics
Computer Graphics
- Definition: Use computer to create images from models and interact with them.

- Depend heavily on the science of:
- Geometry
- Optics
- Physics
- CG includes:
- 3D modeling (Creating the object)
- Shaders (Coloring objects)
- Visualization and rendering (Existing Data Ex: Medical images)
- Animation ( Transformations)
- … Etc
- Movies:
- Animations
-
Visual effects


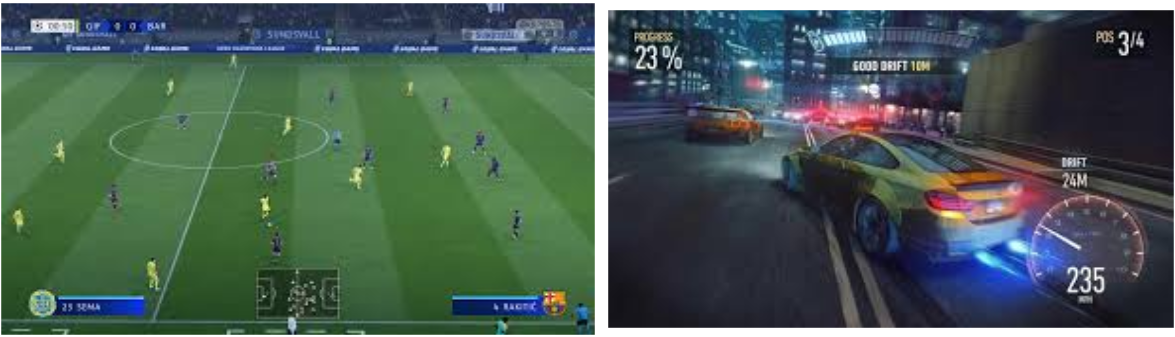
- Video Games:
-
User interaction
-
-
Computer Aided design:

-
Medical Visualization:
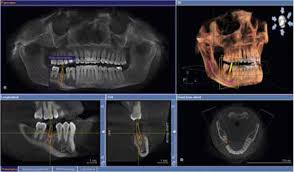
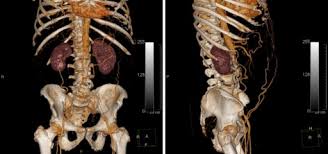
Tools
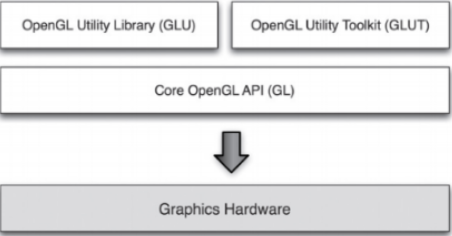
- OpenGL (Open Graphics Library):
- Cross platform API for rendering
- Handle the interaction with GPU (rendering acceleration)
- Low level functionalities for rendering
- OpenGL Utility (GLU) OpenGL Utility Toolkit (glut):
- Higher level functions
-
Window handling ,Camera positioning, interaction

- Visualization toolkit (VTK):
- For volume rendering and medical visualization
- VTK with Qt
- Qt is a Cpp library for GUI and general programming
- From dicom images to 3D volume
- Tissue coloring and selection
-
Navigation and exploration

- Unity Game Engine:
- Drag and drop tool with coding for fast production
-
Cross platform (Desktop and mobiles)

- OpenGL:
- Cross platform application programming interface (API) for rendering
- Handle interaction with GPU to accelerate rendering
- Has low level functionality
- OpenGL Utility (GLU) and OpenGL utility toolkit (glut)
- Provides high level functionalities
- Ex: Camera positioning
- window handling
- keyboard interaction
- OpenGL, GLU and glut are a C API not C++ API (No classes, namespaces)
- Functions of OpenGL starts with gl, for GLU glu, for glut glut
- Data types and dimension of vectors provided to function identified as follow
- f for float, i for integer,
- Ex: glvertex2i(), glvertex3f()
Installation
- Linux Users
sudo apt-get install freeglut3-dev
- Windows Users
-
Download the compiled source files [Here] (https://osdn.net/projects/sfnet_colladaloader/downloads/colladaloader/colladaloader%201.1/glut-3.7.6-bin.zip/).
-
Create a new folder in “C:\” directory, and name it “glut”.
-
Inside “C:\glut”, create two new folders with names “include” and “lib”
-
Create a new folder and call it “gl” inside “C:\glut\include”, copy glut.h” from the unzipped file and passed it here. where you should have : C:\glut\include\gl\glut.h
-
Inside “C:\glut\lib” copy “glut.def ” + “glut32.lib” + “glut32.dll” + “README-win32.txt” from the unzipped file and passed it here. where you should have : So: C:\glut\lib\glut.def, C:\glut\lib\glut32.lib, C:\glut\lib\ glut32.dll, C:\glut\lib\ README-win32.txt
-
Start, Control Panel, System, Advanced, Environment Variables
-
In the “Environment Variables” window and under the “system variables” select “path”, then click “edit” and in the “variable value” label add “C:\glut\lib;”, then click “Ok”
-
restart your computer to make sure that the windows operating system noticed those changes.
-
Go to Visual Studio and create your C++ projectas follow:
- New Project
- Under “Installed” on the left panel; select “Visual C++”, then select “ Win32” ,select from the middle panel “Win32 console application”, rename your project (with a meaningful name, ex: HelloCG), select your path from “Browse”, then click “Ok”.
- In the “Win32 Application Wizard” click “Next”, under “Additional options”select “Empty project”, then click “Finish”
- From “Solution Explorer” window, right click on “Source Files” and chose “Add” then chose “New Item…”
- From the “Add New Item” window, select “C++ File (.cpp)” from the middle panel, then edit the name (ex. main.cpp) …. Now yoou are ready to go with a C++ project withoud open GL
- Go to “Project”, then “Properties” and in the “Configuration Properties” in the left panel chose “VC++ Directories”, then from the right panel edit “Include Directories” and browse to add the path of the C:\glut\include\gl, also edit “”Library Directories” and browse to add “C:\glut\lib”.
Demo 1:
#include <GL/glut.h>
void display(void)
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glBegin(GL_TRIANGLES);
glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); /* blue */
glVertex2i(0, 0);
glColor3f(0.0, 1.0, 0.0); /* green */
glVertex2i(150, 250);
glColor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); /* red */
glVertex2i(300, 0);
glEnd();
glFlush(); /* Single buffered, so needs a flush. */
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutCreateWindow("single triangle");
glOrtho(0, 300, 0, 300, -1, 1); /* Map abstract coords directly to window coords. */
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
then run project on winows or compile in linux By:
gcc -o source source.c -lGL -lGLU -lglut -lm
you should see

Demo 2
#include <GL/glut.h>
void display(void)
{
//Clear color and depth buffers
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// Assign a color to the teapot
glColor3f(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
// Rotation
glRotatef(10, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
glRotatef(10, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
//Draw
glutWireTeapot(1);
//Must swap the buffer in double buffer mode
glutSwapBuffers();
}
void init(void)
{
//Model(Object coordinates), View (Camera coordinates), Projection (Screen coordinates)
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
gluPerspective( /* field of view in degree */ 40.0,
/* aspect ratio */ 1.0,
/* Z near */ 1.0, /* Z far */ 10.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
gluLookAt(0.0, 0.0, 5.0, /* eye is at (0,0,5) */
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, /* center is at (0,0,0) */
0.0, 1.0, 0.); /* up is in positive Y direction */
}
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
//Use Double buffer, RGB, and depth test mode
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH);
glutCreateWindow("Green 3D Teapot");
init();
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
compile the same as above you should see
