Week 10: Merge and Quick Sorting, more on Dijkstra, and the Final Project
- Divide and Conquer Strategy: The Merge Sorting
- Divide and Conquer Strategy: The Quick Sorting
- The Shortest Path (TSP) Problem using Dijkstra’s
- Next Week: Workshop
Divide and Conquer Strategy: The Merge Sorting
We can employ the divide and conquer principle in sorting arrays. Divide and Conquer principle basically divides the big problem into smaller sub-problems an attempts to exploit the solutions of smaller problems to obtain the solution of the big problem.
| Merge Sort animated |
|---|
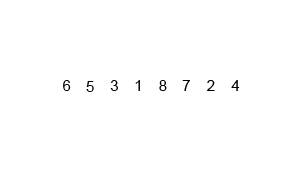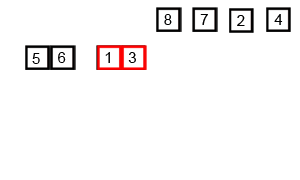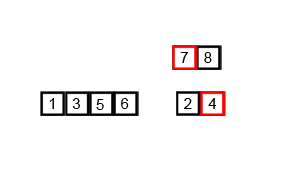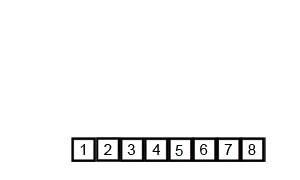 |
| Creative Commons |
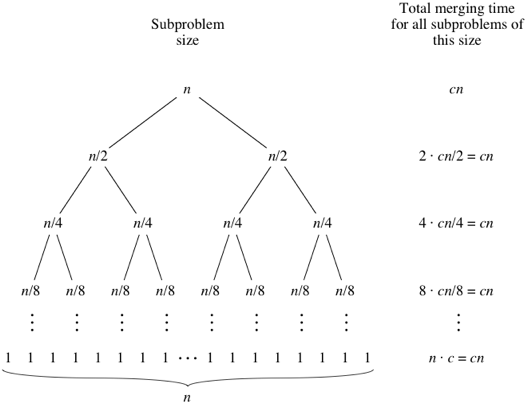
Complexity Analysis
| Merge Sort Analysis via diagram |
|---|
 |
| CC-BY-NC-SA |
For advanced details, see Analysis of merge sort | Khan Academy.
Implementation
Divide and Conquer
void mergeSort( std::vector< double > &a , int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
int mid=(low+high)/2;
// Split the data into two half.
mergeSort(a, low, mid);
mergeSort(a, mid+1, high);
// Merge them to get sorted output.
merge(a, low, mid, high);
}
}
Combine the small solutions
void merge( std::vector< double > &a , int low, int mid , int high )
{
int n1 = mid - low + 1;
int n2 = high - mid;
std::queue<double> left, right;
for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++)
left.push( a[low + i] );
for (int i = 0; i < n2; i++)
right.push( a[mid + 1 + i]);
int offset = low;
while( !left.empty() && !right.empty())
{
if( left.front() < right.front())
{
a[ offset ] = left.front();
left.pop();
}
else
{
a[ offset ] = right.front();
right.pop();
}
++offset;
}
while( !left.empty())
{
a[ offset++ ] = left.front();
left.pop();
}
while( !right.empty())
{
a[ offset++ ] = right.front();
right.pop();
}
}
John Von Neumann
| John Von Neumann (1903-1957) |
|---|
 |
Neumann has made tremendous scientific contributions in the modern history. His contributions were mainly foundational in several mathematical fields, such as:
- Game Theory
- Quantum Mechanics
- Ergodic Theory
- Computer Science
He also worked in the Manhattan Project.
Divide and Conquer Strategy: The Quick Sorting
Like Merge Sort, Quick Sort utilizes divide and conquer strategy; it divides the big problems into smaller sub-problems.
| Quick Sort animated |
|---|
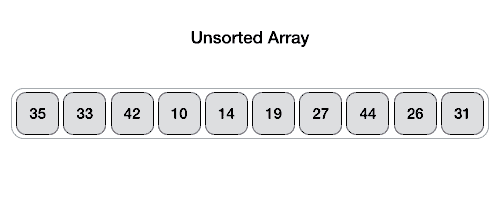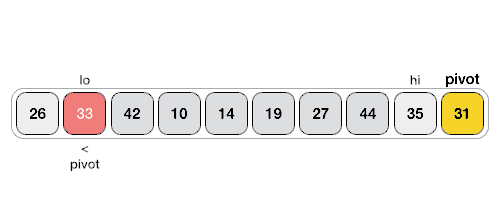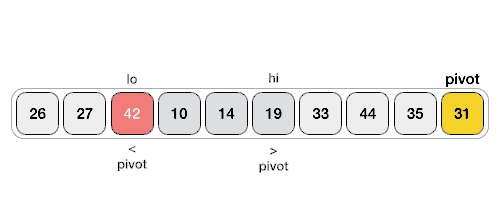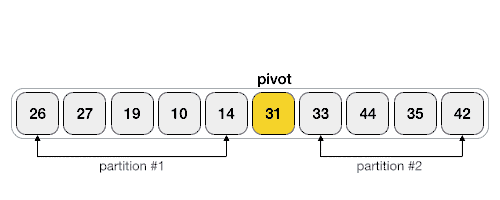 |
| source |
Pivot selection:
- first element
- last element
- median
- random
QuickSort: Implementation
void quickSort( std::vector< double > &a, int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
int pIdx = partition(a, low, high);
if (low < pIdx)
quickSort(a, low, pIdx - 1); // Before pi
if (high > pIdx)
quickSort(a, pIdx + 1, high); // After pi
}
}
int partition( std::vector< double > &a, int low, int high )
{
int pivot = a[low];
int i = low + 1, j = high;
while (i <= j)
{
while (i <= j && a[i] < pivot)
++i;
while (i <= j && a[j] > pivot)
--j;
if (i <= j)
std::swap(a[i++], a[j--]);
}
std::swap( a[--i] , a[low] );
return i;
}
The source code:
git clone git@github.com:sbme-tutorials/sbe201-merge.git
The Shortest Path (TSP) Problem using Dijkstra’s
| Dijkstra animated |
|---|
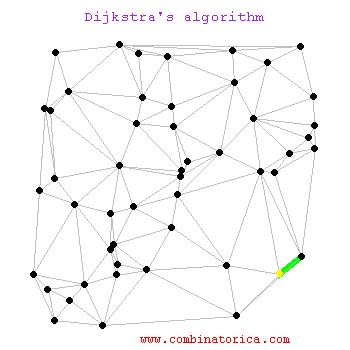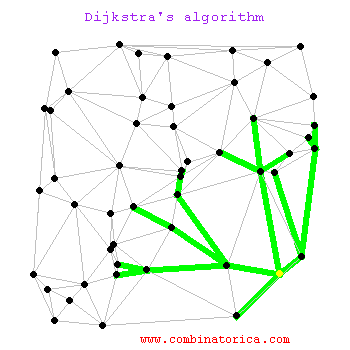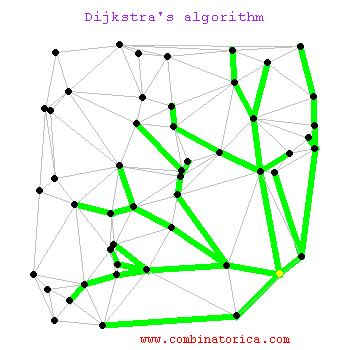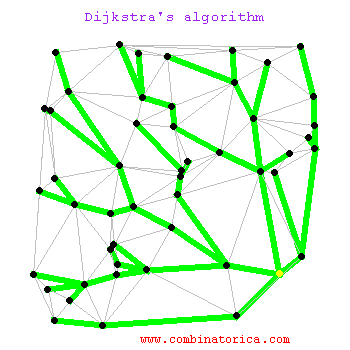 |
| source |
Read Finding The Shortest Path, With A Little Help From Dijkstra
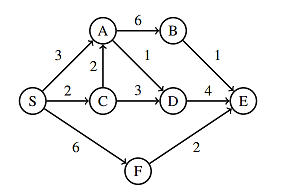
Dijkstra: Exercise
Edsger Wybe Dijkstra
| Edsger Wybe Dijkstra (1930-2002) |
|---|
 |
Simplicity is prerequisites for reliability — Dijkstra
Next Week: Workshop
Prerequisites
- Install Qt and QtCreator.
- Install CMake.
- Coursera Account.
- Install Jekyll.
- Install Latex and TexMaker.