Week 1 - Part 2: Basics of Git and Github
Problem Definition
Recall the example of area problem from Part 1: C++ Basics.
Imagine the case when Asem and Ahmed need to collaborate on this project. Such that:
- Asem generates the biolerplate/skeleton (i.e the files and the main function) of the project.
#include <iostream>
namespace rectangle
{
// No implementation yet!
}
namespace triangle
{
// No implmenetation yet!
}
int main()
{
double rectangleArea = rectangle::area( 12.9 , 2.5 );
double triangleArea = triangle::area( 4.0 , 3.0 );
std::cout << "Rectangle area: " << squareArea << std::endl
<< "Triangle area: " << triangleArea << std::endl;
}- Ahmed has to implement the rectangle area function \(A = w h\).
- Asem has to implement the triangle area function \(A = \frac{bh}{2}\).
Possible Awful Scenarios:
- Asem sends an Ahmed fax containing the skeleton, then Ahmed sends back the skeleton with the
square::areafunction implemented, and so on. - A-like scenario, but through facebook, e-mail, or dropbox!
- They pass USB disk back and forth!
- They sit together to finish the project!
And wait a minute:
- What if we have a team of 8 members.
- What if your application was as big as 20K lines of code across tens of files.
Version Control Systems
- Keep track of all the changes that happened (No lost work).
- Many Developers can work on the same file at the same time.
- The Version Control System will handle conflicts if possible, if not, it will ask the developers to check it.
Popular Version Control Systems
- Git (we will use this)
- Mercurial
- Subversion (SVN)
Git

- Linus Torvaldos developed Linux Kernel in 1991.
- Torvalds and others developed Git for management of Linux Kernel source in 2005.
- Git is Free and Open Source.
- Great community support. You can always search in Quora and Stackoverflow for problems you face.
Typical Git Cycle
For your first experience with git, refer to this workflow.
- [First Time Only] Create/Clone Repository to your disk, so you have a local copy.
- [Optional] Create a branch giving it a name (e.g your new feature/function name).
- Make changes to your source (edit/add new file).
- Add new files to your repository system. (You already created the files physically, but you need to ask the git repository to take control of your new file).
- Commit your changes.
- Get latest updates.
- Resolve any conflict (if any).
- Push to the remote repository.
Create/Clone Repo
- Case 1: New Repository.
$ git init
$ git remote add [name] [URL]- Case 2: Existing Repository.
$ git clone [URL]Create Feature Branch
$ git checkout –b [branch name]Track Files
It is recommended to add file by file, so apply this command to all your application souce files, exclude any executable files or files generated by the compiler.
$ git add [file name]Or, alternatively, do it once for all files (not recommended, but it is up to you anyway). Just make sure you don’t add any executable or compiler generated file. In assignments, you may jeopridize your score if you added any executable files in the repository.
$ git add *Commit Changes
Please write a message that you can understand (e.g briefly, indicate your changes in the repository e.g “implementing square::area function”).
$ git commit -a -m “Message”Get latest updates
Before you publish your changes to the remote repository, update your repository in case some member of your team has made changes before you.
$ git pull [remote name] [branch name]By default, remote name is origin and branch name is master, unless you made a new branch you are working on with your teammates.
Push Changes
To publish your changes to your teammates on the remote repository:
$ git push [remote name] [branch name]Similarly, by default, remote name is origin and branch name is master, unless you made a new branch your are working on with your teammates.
But what is Remote Repository, What do you mean
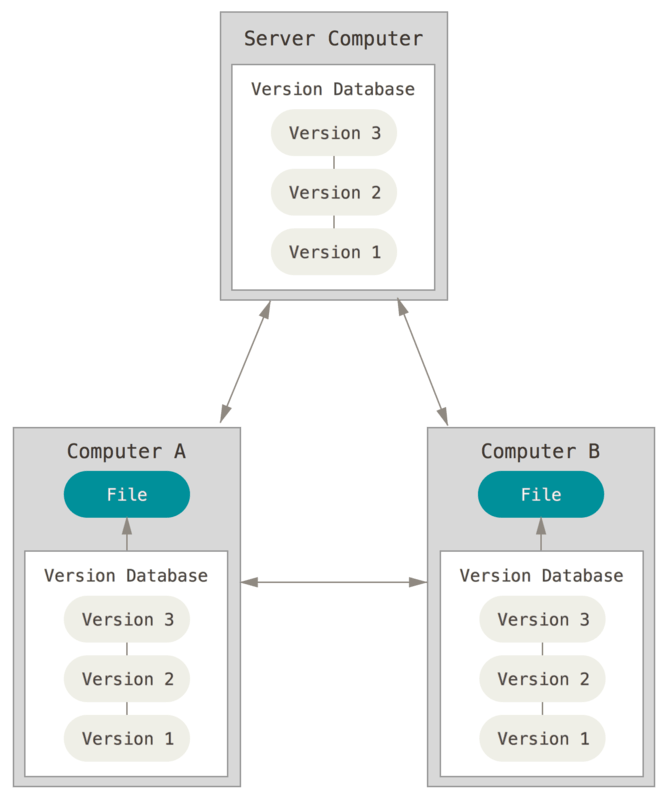
This photo is from official git website.
Git in the cloud
Popular servers offering free remote repository hosting:
 +
+
- Github is offering you unlimited repository, but in public.
- To get the advantage of private repositories, but with charge of 7$/month (~ 125 EGP). Unless you are student. Beware of the power of having institutional e-mail! I advice you to request an institutional e-mail from the faculty (maybe from the students affairs). Much more offers are free for student at Github (see educational page, student pack, how to apply).
Hands-on
Trying git online with interactive console
Follow this nice interactive tutorial from Github for using Git: Try Git.
Trying git on your machine
Installing Git on your machine
Issue the following command in your terminal.
$ sudo apt-get install gitOnce installed, let the Git know your name and your email. So from now on, any commit or changes you make to your source code will be signed by your name and email. This is very useful when working with teams!
$ git config --global user.name "John Doe"
$ git config --global user.email johndoe@example.comGenerate the skeleton of your project
- Open the terminal (
Ctrl+Alt+L). The terminal will launch on your home directory by default (/home/yourname). - Create a directory with name
hello-gitusing the following command:
$ mkdir hello-git- Change directory from home to
hello-gitusing:
$ cd hello-git- Open the text editor with new file called
einstein-happiness-theory.txt(For example, by the graphicalgeditor the console-basednano), using the following command:
$ gedit einstein-happiness-theory.txt- In the file, copy the following saying by Albert Einstein: “A calm and modest life brings more happiness than the pursuit of success combined with constant restlessness,”.
- Close the editor and save the file.
- In your terminal, initialize a git repository to watch and take control of your source file, using the following command:
$ git init- Let’s ask our new git repository (repo for short), to take control of our new file
einstein-happiness-theory.txt, using the following command:
$ git add einstein-happiness-theory.txt- Let the repo confirm your new changes (i.e adding a new file to the repo system), and leave a message indicates briefly What is the change about.
$ git commit -a -m "Adding a file containing a saying by Albert Einstein"- Optional: if you wish to have a remote repository to save your new project on the cloud, make sure you have registered with Github or Bitbucket. For example, for bitbucket, follow these intructions to create a repository on bitbucket. After making your repository, you should find some instructions titled Get started with command line then select I have an existing repository and follow the instructions.