Assignment 3 - Part 1: Arrays
Prerequisites
- Required: Read the notes of the first week: [Part 1: Static Arrays and Dynamic Arrays] [Part 2: Command Line Arguments and Compilation of Multiple Files].
Objectives
- Revisiting namespaces, references, and pointers.
- Work with multiple files.
- Work with multiple applications.
- Realize the dependencies between files.
-
Implement basic array operations:
- print (traverse)
- mean
- variance
- max
- min
- counters
-
Work with biological data in array structures.
- Analyze DNA
- Return the complementary sequence of DNA
- Count a specific base pair in DNA
- Analyze ECG: mean, variance, max, and min.
- Compilation of multiple files.
Deadline
Sunday 4/3/2018 11:59 PM.
Assignment: Part 1
Go to the assignment page and git clone your own repository.
Overview
You will learn how to work with multiple files. We will write our interesting functions in header files, and then use these functions in our interesting applications.
The header files (library)
We will work and implement our logic inside these files:
mathematics.hppto contain some mathematical functions likecalculation.arrays.hppto contain our array functions.ecg.hppto contain analysis functions on ECG.dna.hppto contain analysis functions on DNA.
Our source files of our applications that we are going to compile into useful and very important applications:
calculator.cppto implement the Calculator application, and depends onmathematics.hpp.heron.cppto implement a simple application that implements Heron Formula, and also depends onmathematics.hpp.analyzeECG.cppto implement very useful application for ECG Analysis, depends onecg.hpp.analyzeDNA.cppto implement very useful application for DNA Analysis, depends ondna.hpp.
You will find a useful header file helpers.hpp, I don’t recommend you to try understanding it before week 6. We will just use two functions from helpers.hpp to load our DNA and ECG files from hard disk.
Dependency Graph
By the way, keep in mind, that application source files that are compiled into executable files, has to be:
- including a
mainfunction. Eachmainfunction is a simply program entry point. - and
mainfunction should be existing in a.cppfile.
You will also realize our header files begin and ends with
#ifndef MATHEMATICS_HPP
#define MATHEMATICS_HPP
// includes of external headers here
// Your functions here
#endif // MATHEMATICS_HPP
No worries, they are called header guards. Will be explained on next tutorial on Sunday. But just consider them as a skeleton (boilerplate) code.
Requirement 1: mathematics.hpp file
- R1.1 (Done for you) Make a
namespace mathematicsthat will contain our functions. - R1.2 Implement our
calculationfunction using either if, else if, else or switch-case. - R1.3 Implement Heron Formula, that is used to compute the triangle area given its three sides, hmmmm very interesting.
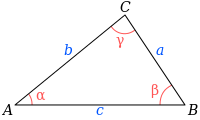
where s is the semiperimeter of the triangle; that is,
\[s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}.\]Use this function declaration:
double heron( double a , double b , double c )
{
// Logic here
}
You also need to #include <cmath> as an external header, to use std::sqrt function that computes the square root.
- R1.4 It is your job now to implement the
mainfunction inheron.cppfile. It is required to make the Heron Formula application to receive the three parameters of the triangle through terminal. So you will retrieve the three parameters through theargvinmainfunction. Remember that you will need to usestd::atoffunction and#include <string>. To usemathematics::heron, add#include "mathematics.hpp". Hint, you may cheat fromcalculation.cppsource file (but with receiving three doubles in this case).
Requirement 2: arrays.hpp file
- R2.1 Make a
namespace arraysthat will contain our functions. - R2.2 Implement a function that prints all array elements on terminal, using the following declaration:
void printAll( double *base , int arraySize )
{
// Logic here
}
- R2.3+R2.4 Implement a function that returns the maximum element and another one for minimum element, using the following declarations:
double maxArray( double *base, int arraySize )
{
// Logic here
}
double minArray( double *base, int arraySize )
{
// Logic here
}
- R2.5+R2.6 Implement a function that returns the mean (average) of array elements and another one that returns the variance, using the following declaration:
double meanArray( double *base , int arraySize )
{
// Logic here
}
double varianceArray( double *base, int arraySize )
{
// Logic here
// Hint: use meanArray ;)
// Do you need a square function?
// Maybe you can implement one in mathematics.hpp
// then include "mathematics.hpp" to use mathematics::square here
}
If you don’t know variance,
\[var = \frac{1}{N} \sum_{n=1}^{N} ( \text{mean} - x_i )^2\]Requirement 3: ecg.hpp file
- R3.1 Make a
namespace ecgthat will contain our function. - R3.2 Make a function that computes the average, variance, max, and min of ECG signal. But these are not single variables so we can return. Alternatively, we will use 4 reference variable in function declaration.
void analyzeECG( double *base , int arraySize , double &mean, double &variance, double &max, double &min )
{
// Logic here (4 lines)
}
Use the four functions we already implemented in arrays.hpp. Accordingly, four lines are sufficient to do this job. And yes, don’t forget to #include "arrays.hpp" in the current header file.
Requirement 4 (Bonus): dna.hpp file and revisiting arrays.hpp file
Revisit arrays.hpp file
- R4.1 Make a function that counts a given character in array of characters, using the following declaration:
int countCharacter( char *basePointer , int size , char query )
{
// Logic here
}
Now dna.hpp file
- R4.1 Make a
namespace dnathat will contain our functions. - R4.2 Implement
complementaryBaseyou did in the first week using either if, else if, else or switch-case, with the following declaration:
char complementaryBase( char base )
{
// Logic here
}
- R4.3 Implement
complementarySequencefunction that returns the complementary DNA sequence.
Please beware that the double strands of our DNA are directional, and they have opposite directions.
For example, the sequence ACG has a complementary sequence CGT, not TGC.
So in your for loop, you may read the original sequence from begining, and write the complementary sequence starting from the end of the complementary sequence array.
By the way, you have to allocate the complementary sequence on the heap (dynamic array) at the begining of function (using the given size).
Use the following declaration:
char * complementarySequence( char *base, int size )
{
// Your logic here
}
- R4.4 Implement
analyzeDNAfunction that counts the 4 bases in a sequence, and returns the complementary sequence. Again, you have four counters and a complementary sequence. So you only return the complementary sequence, and the counters will saved back to reference integers. Remember to usearrays::countCharand to#include "arrays.hpp"in the current file. Use the following declaration:
char *analyzeDNA( char *base, int size, int &countA, int &countC, int &countG, int &countT )
{
// Your logic here (5 lines).
}
Submission and Bonus Policy
- As usual, commit and push your changes.
- Requirement 4 is completely counted as bonus.
- Also, you may obtain bonus with correct logic by consistent adoption of KISS and DRY principles. Also, make your code clean, well-aligned, and use descriptive variable names.
Generating Executables and Testing Output
Compiling and Testing calculator.cpp
$ g++ calculator.cpp -o Calculator
$ ./Calculator 24 / 7
3.42857
$ ./Calculator 24 \* 7
Note: asterisk * is a special character for the terminal. You need to explicitly use \* to specify multiplication operation.
Compiling and Testing heron.cpp
$ g++ heron.cpp -o Heron
$ ./Heron 3 4 5
6
Compiling and Testing heron.cpp
$ g++ heron.cpp -o Heron
$ ./Heron 3 4 5
6
Compiling and Testing analyzeECG.cpp
We compile and test using an ECG dataset stored in datasets/ecg_data.txt.
Our application in the main function loads data from the file then use ecg::analyzeECG
function implemented in ecg.hpp.
$ g++ analyzeECG.cpp -o AnalyzeECG
$ ./AnalyzeECG datasets/ecg_data.txt
ECG average : 0.785639
ECG variance: 0.00780314
ECG range : (0,1.288)
Compiling and Testing analyzeDNA.cpp
We compile and test using a DNA dataset stored in datasets/genetic_data.txt.
Our application in the main function loads data from the file then use dna::analyzeDNA
function implemented in dna.hpp.
$ g++ analyzeDNA.cpp -o AnalyzeDNA
$ ./AnalyzeDNA datasets/genetic_data.txt
Adenine (A) content:75
Guanine (G) content:84
Cytocine(C) content:83
Thymine (T) content:76
Complementary Sequence:
CCAGTATTTGACAGGCTGGACTGAGCTACTTGCCGTTCCGGGATAAGTAGTTCAGACAGGCTGCCCACAACGTACAAAGACGGCCAGTTCTCCGCATATCGCGGCATTCGAGTCCGGCAAATAGCGAGTTAGCCTCTTCTTGCGCTGGACCTTTTCTAGCCGCATGACTAGTTGCCAAGGCTGAAGCCCAAGTTAGAGTGGCATGTAGTCCCTCAGTGAAGGGAATGGCTCGAGTCGAAGCAGCTTACAGCACAGCTCTCGACTCCTAATTGGGTCGAAGCCTATCAACTATCCACGTAGTGTCCAGTATTTGACAGT